반응형
Stack
- int 배열을 사용해서 정수를 저장하는 Stack을 구현하세요.
- void push(int data)를 구현하세요.
- int pop()을 구현하세요.
- ListNode head를 가지고 있는 ListNodeStack 클래스를 구현하세요.
- void push(int data)를 구현하세요.
- int pop()을 구현하세요.
stack은 제한적으로 접근할 수 있는 나열 구조이다. 접근 방법은 언제나 목록의 끝에서만 일어나 끝먼내기 목록(Pushdown list)이라고도 한다. 한 쪽 끝에서만 자료를 넣거나 뺄 수 있는 선형 구조로 후입선출(LIFO - Last In First Out)의 구조를 이루고 있다.
- push
자료를 밀어 넣는것 - pop
자료를 꺼내는것, 가장 최근에push한 자료부터 나오게 된다.
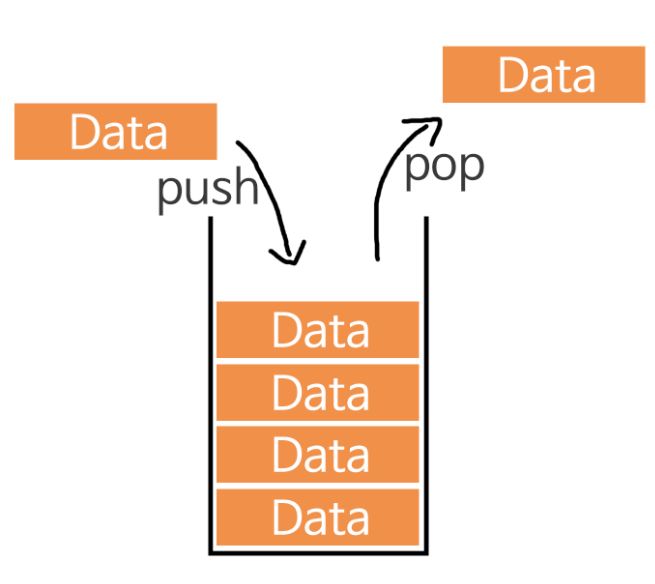
구현
public class ArrayStack {
private int[] data;
private int stackSize;
private int dataSize;
public ArrayStack() {
this.data = new int[10];
this.stackSize = 10;
this.dataSize = 0;
}
public ArrayStack(int stackSize) {
this.stackSize = stackSize;
this.data = new int[stackSize];
this.dataSize = 0;
}
public void push(int data) {
if (dataSize + 1 == stackSize) {
int[] newStack = new int[stackSize + 10];
for (int i = 0; i < stackSize; i++) {
newStack[i] = this.data[i];
}
this.data = newStack;
}
this.data[dataSize++] = data;
stackSize += 10;
}
public int pop() {
if (this.dataSize == 0) {
System.out.println("데이터가 없습니다.");
return -1;
}
return data[--dataSize];
}
public void print() {
if (this.dataSize == 0) {
System.out.println("데이터가 없습니다.");
return; }
for (int i = 0; i < dataSize; i++) {
System.out.println(data[i]);
}
}}테스트
class ArrayStackTest {
@Test
void 푸시() {
ArrayStack stack = new ArrayStack();
stack.push(10);
stack.push(20);
stack.push(30);
stack.push(40);
stack.push(50);
stack.print();
}
@Test
void 팝() {
ArrayStack stack = new ArrayStack();
stack.push(10);
stack.push(20);
stack.push(30);
stack.push(40);
stack.push(50);
System.out.println(stack.pop());
stack.print();
}
}구현
public class LinkedStack {
ListNode node;
public LinkedStack() {
node = new ListNode();
}
public LinkedStack(int data) {
this();
node.add(node, new ListNode(data), node.getSize());
}
public void push(int data) {
node.add(new ListNode(data));
}
public int pop() {
try {
return node.remove(node, node.getSize() - 1).getData();
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
return -1;
}
}
}테스트
class LinkedStackTest {
@Test
void 푸시() {
LinkedStack stack = new LinkedStack();
stack.push(10);
stack.push(20);
stack.push(30);
stack.push(40);
stack.push(50);
stack.push(60);
Assertions.assertEquals(60, stack.pop());
}
@Test
void 팝() {
LinkedStack stack = new LinkedStack();
stack.push(10);
stack.push(20);
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.pop());
}
}
참고
https://github.com/jongnan/Java_Study_With_Whiteship/blob/master/week4/week4_3_and_4.md
https://blog.naver.com/hsm622/222159930944
https://ko.wikipedia.org/wiki/%EC%8A%A4%ED%83%9D
반응형
'TIL' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Queue 구현해보기 (0) | 2021.01.03 |
|---|---|
| LinkedList 구현해보기 (0) | 2021.01.02 |
| Windows Terminal에서 ubuntu 사용하기 (0) | 2020.12.10 |
| [TIL] 200828 간단한 IntelliJ 단축키 팁 (0) | 2020.08.28 |
| [TIL] 200824 JAVA. HashMap의 getOrDefault() (0) | 2020.08.24 |